Molding plastic is a versatile material used in various industries. It is made through the process of shaping raw plastic resin into desired forms. According to John Smith, an expert in the molding plastic industry, "Molding plastic is critical for innovation in product design." His insights illustrate the importance of molding plastic in creating functional and aesthetic products.
The applications of molding plastic are vast. From consumer goods to medical devices, this material plays a vital role. It can be molded into intricate shapes and sizes, allowing for creativity in design. However, the molding plastic industry faces challenges, including waste management and sustainability. These issues require attention from manufacturers and consumers alike.
Despite its advantages, the process isn't without flaws. Molding plastic can lead to defects and inconsistencies. Such issues can affect product quality and longevity. Addressing these imperfections is essential for advancing the industry. Molding plastic holds immense potential, but ongoing reflection is necessary for improvement.

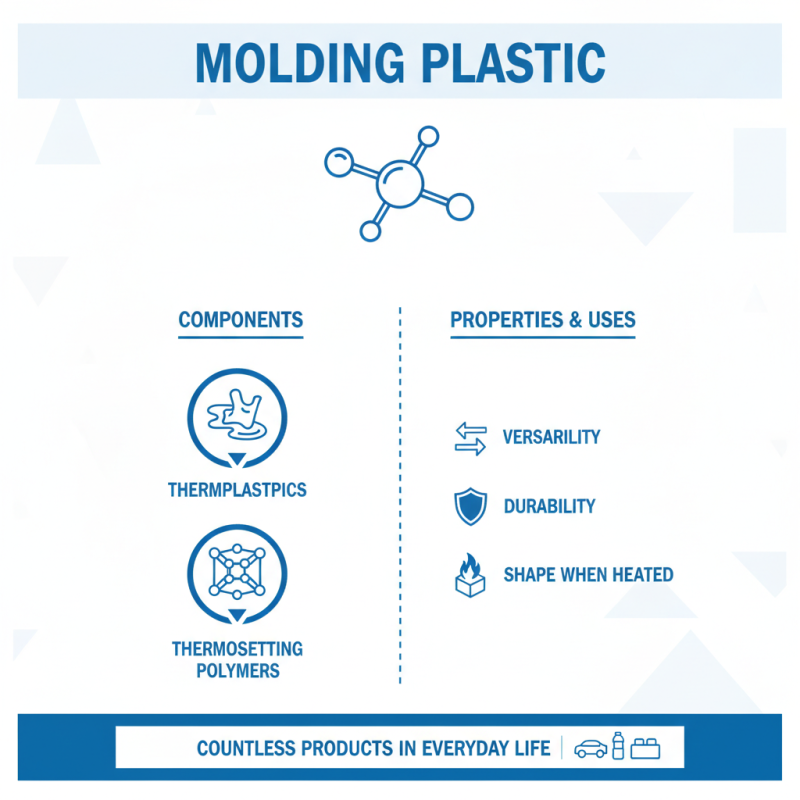
Molding plastic is a synthetic material used for various applications. It is known for its versatility and durability. The primary components of molding plastic include thermoplastics and thermosetting polymers. These materials can be shaped and formed when heated. Their properties make them suitable for countless products in everyday life.
One of the essential properties of molding plastic is its strength. It can endure significant stress without breaking. Molding plastic also resists moisture, which enhances its usability in various environments. However, molding plastic can sometimes be brittle, leading to unexpected breakage under certain conditions. Factors like temperature and stress levels can affect its performance.
Coloring agents and additives can enhance the visual appeal of molding plastic. This allows for a wide range of designs. Despite its benefits, molding plastic has environmental drawbacks. Many types are not biodegradable, raising concerns about sustainability. Manufacturers must explore eco-friendly alternatives or recycling methods for better environmental impact.
Molding plastics come in various types, each serving different manufacturing needs.
Injection molding is popular. It allows for complex shapes with high precision.
This method uses heat to melt plastic pellets. The molten plastic is injected into molds. Once cooled, it forms hard, detailed parts.
Molding plastic plays a crucial role across various industries. In automotive manufacturing, it’s used to create interior components, dashboards, and bumpers. These parts need to withstand wear and tear while also looking appealing. The ability to customize shapes and colors makes molding plastic a popular choice for these applications.
In the consumer goods sector, molding plastic produces everyday items like containers, toys, and kitchenware. This method allows for mass production, making it cost-effective for businesses. However, not all designs are practical. Sometimes, they lack durability or are difficult to recycle. These challenges prompt manufacturers to rethink their designs.
Medical devices also rely heavily on this material. Molding plastic creates items like syringes, IV bags, and surgical trays. These products must meet strict safety standards. Yet, the focus on appearance can sometimes overshadow functionality. Identifying and addressing these flaws is crucial for innovation.
Molding plastic is a complex process. Various techniques and equipment are involved in creating molded products. One common technique is injection molding. In this process, molten plastic is injected into a mold cavity. It cools and hardens, forming a specific shape.
Another method is blow molding. This technique is used for hollow items like bottles. Air is blown into a plastic tube, expanding it against the mold. Each process has its unique challenges. For instance, injection molding requires precise temperature control. If the temperature is too high, the plastic may degrade.
Thermoforming is also a popular technique. It involves heating a sheet of plastic until it's pliable. Then, it is formed into a mold by vacuum or pressure. This method is often used for packaging. However, it can lead to inconsistencies in thickness. The equipment used varies in complexity. Advanced machines can automate many steps. But, this can increase initial costs. Balancing efficiency and quality is vital in production.
| Molding Technique | Description | Applications | Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Injection Molding | A process where molten plastic is injected into a mold cavity. | Consumer products, automotive parts, medical devices. | High production efficiency, complex geometries, minimal waste. |
| Blow Molding | A method for producing hollow plastic parts by inflating a hot tube of plastic. | Bottles, containers, and tanks. | Fast production speed, lightweight products, low cost. |
| Rotational Molding | A technique where plastic powder is heated and rotated to form a hollow part. | Large tanks, playground equipment, and automotive components. | Low tooling costs, good for large parts, even wall thickness. |
| Thermoforming | A process where a plastic sheet is heated until pliable and then formed over a mold. | Packaging, trays, and disposable cups. | Quick setup, low cost for short runs, minimal waste. |
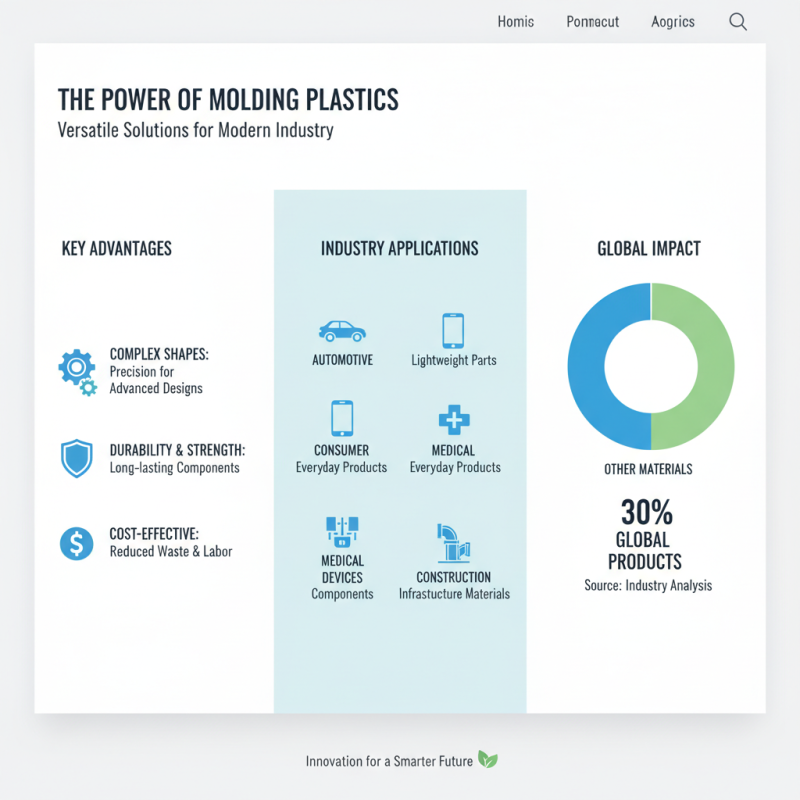
Molding plastics play a crucial role in various industries, from automotive to consumer goods. The advantages they offer are significant. For instance, molding processes can create complex shapes that are often impossible with traditional materials. According to a recent industry analysis, molded plastics account for approximately 30% of all plastic products manufactured globally.
However, the use of molding plastics also presents challenges. One key issue is environmental impact. An estimated 7.9 million tons of plastic waste are generated each year due to faulty production or improper disposal. While recycling initiatives are growing, many molded plastics are not biodegradable. Another challenge is the initial cost. The setup for injection molding can be expensive, often deterring small businesses from entering the market.
Moreover, the quality of molded parts can vary. Inconsistent heating and cooling during production can lead to defects. This inconsistency affects durability and performance, prompting manufacturers to implement stricter quality controls. Balancing these advantages and challenges is vital for maximizing the benefits of molding plastics, but it's an ongoing process that requires constant attention and adaptation.