Casting plastic has become an essential process in various industries, ranging from manufacturing to art and crafts. Understanding how to choose the right casting method is crucial for achieving the desired results, whether it be molds for industrial components or decorative items. Each casting technique offers unique advantages and is suited to different applications, making it vital for professionals and hobbyists alike to make informed decisions based on their specific needs.
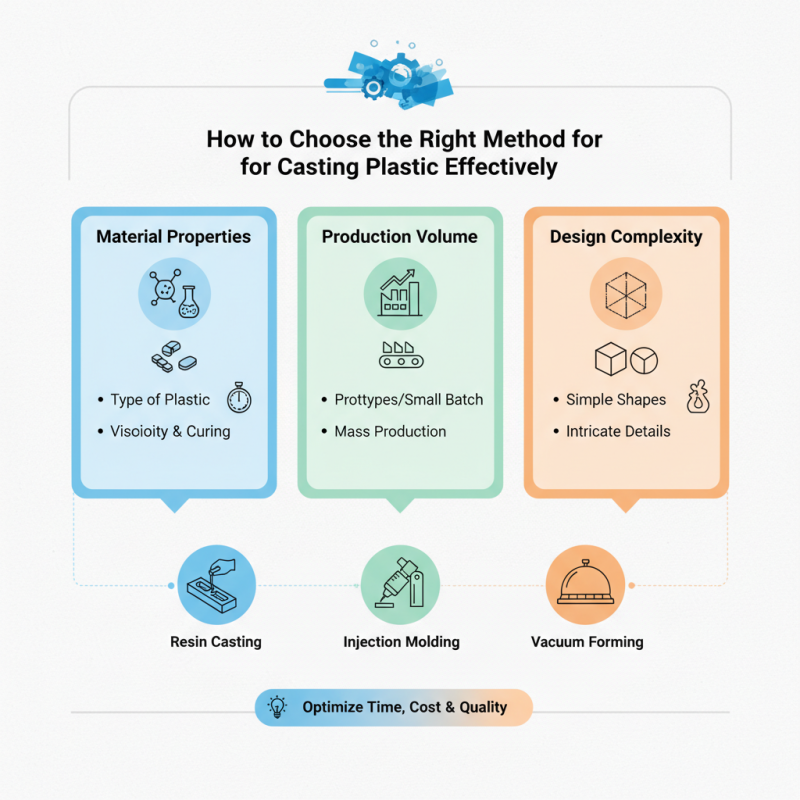
In navigating the various options for casting plastic, factors such as material properties, production volume, and design complexity should be carefully considered. Techniques like resin casting, injection molding, and vacuum forming each have their own strengths and limitations, influenced by aspects such as the intricacy of the design and the intended use of the final product. By exploring these different methods, one can not only enhance the quality of their production but also optimize time and cost efficiency.
As we delve into the specifics of casting plastic, we will aim to provide a comprehensive understanding of the techniques available, guiding you towards selecting the most suitable method for your project requirements. With the right knowledge and approach, the potential of casting plastic can be fully realized, leading to innovative solutions and exceptional end results.
When considering the various methods for casting plastic, it is essential to understand the distinct characteristics and applications of each type. The two primary methods of plastic casting are polyurethane casting and silicone casting, each with its own advantages and ideal use cases. According to a report by Grand View Research, the global market for polyurethane is expected to reach USD 60.75 billion by 2025, highlighting its growing popularity in various applications. Polyurethane casting is favored for its flexibility and durability, making it suitable for products requiring intricate details and resilient performance.
On the other hand, silicone casting offers a different set of benefits, particularly in the realm of creating prototypes and models. The ability of silicone to capture fine details while maintaining high elasticity makes it an excellent choice for artists and manufacturers seeking to make precise replicas or molds. A study published by Mordor Intelligence indicates that the silicone market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 4.5% between 2021 and 2026, driven by the increasing demand in construction and automobile industries. Understanding these different methods equips manufacturers and designers with the knowledge needed to select the most effective casting strategy tailored to their specific applications and desired outcomes.
When selecting the appropriate method for casting plastic, understanding the material properties is crucial to the successful application of casting techniques. Different plastics exhibit varying characteristics that can significantly influence the choice of casting process. For instance, thermoplastics like ABS and polycarbonate are known for their excellent impact resistance and thermal stability, which can be beneficial in applications requiring durability. According to a report by the Plastics Industry Association, thermoplastic consumption has grown by approximately 3-5% annually, highlighting the increasing demand for robust materials in manufacturing processes.
Evaluating the mechanical and thermal properties of plastics can aid in determining the best casting method. For instance, the tensile strength of acetal copolymer is around 90 MPa, which makes it suitable for precision parts that necessitate high strength and low friction. A comprehensive study published in the Journal of Advanced Materials indicates that casting methods like injection molding can yield superior dimensional accuracy for complex geometries when paired with appropriate high-performance plastics. Furthermore, understanding the fluidity of the material, typically represented by its melt flow index (MFI), is essential. Materials with higher MFI are generally more suited to injection molding, while lower MFI options are preferable for casting processes like resin casting, where detail fidelity is paramount.
| Material Type | Melting Point (°C) | Density (g/cm³) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Flexural Modulus (GPa) | Impact Resistance (J/m) | Casting Method Compatibility |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polypropylene (PP) | 160 | 0.90 | 30-40 | 1.0-1.5 | 34 | Injection Molding, Thermoforming |
| Polycarbonate (PC) | 150 | 1.20 | 60-70 | 2.0-2.5 | 850 | Injection Molding, Casting |
| Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) | 105 | 1.04 | 30-40 | 2.0 | 40 | Injection Molding, 3D Printing |
| Polyethylene (PE) | 130 | 0.92 | 20-30 | 0.2-0.5 | 10 | Injection Molding, Blow Molding |
| Polystyrene (PS) | 100 | 1.05 | 40-60 | 3.0 | 25 | Casting, Injection Molding |
When choosing the right method for casting plastic, assessing production volume and cost factors is essential to ensure maximum efficiency and profitability. For instance, according to a recent report by Grand View Research, the global plastic molding market is projected to reach $600 billion by 2025, highlighting the increasing demand for various plastic products. Understanding your anticipated production volume can significantly influence the choice of casting method, whether it involves injection molding, blow molding, or rotational molding.
Tips: Evaluate your production needs carefully. If you anticipate high volume production, injection molding may be the most cost-effective solution, providing the ability to produce thousands of identical parts quickly and with a high degree of precision. Conversely, for lower production volumes, rotational molding can offer lower initial costs without sacrificing quality, particularly for larger items.
Moreover, it's crucial to consider the overall cost implications of each method. For example, the initial setup costs for injection molding can be significant, as the creation of molds requires a substantial investment. According to a study from the Society of Plastics Engineers, while the per-unit cost decreases with volume in injection molding, the same may not hold true for other methods like hand casting or 3D printing, where costs might remain consistent regardless of the scale. Therefore, balancing initial costs against potential long-term savings is vital for making an informed decision.
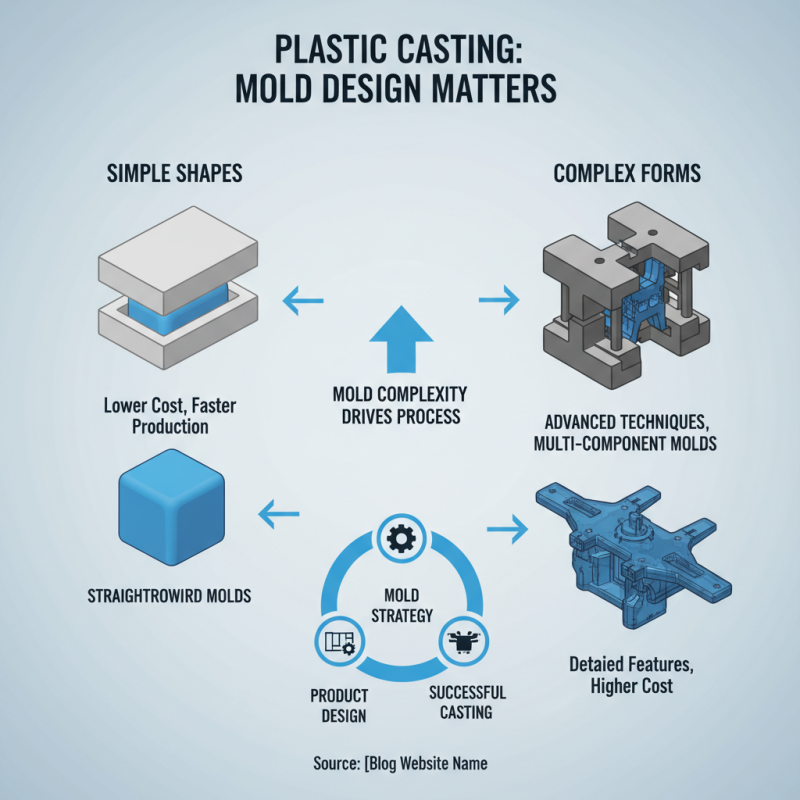
When selecting the right method for casting plastic, the design and complexity of the mold play a pivotal role in determining the overall success of the process. The mold design should align with the specific characteristics of the desired end product, including its dimensions, shape, and intricacy. Simple shapes may benefit from straightforward mold designs, which can be produced quickly and at a lower cost. Conversely, more complex forms often require advanced techniques and attention to detail, potentially involving multiple components in the mold to accommodate undercuts and intricate features.
Moreover, the complexity of the mold significantly influences the casting technique chosen. For intricate designs, methods such as injection molding may be more suitable, as they offer precision and the capacity to produce high volumes of detailed parts. On the other hand, simpler designs might be effectively produced using techniques like blow molding or rotational molding, which can provide economic benefits without compromising quality. Ultimately, a well-considered mold design that takes into account the complexity of the product is crucial for selecting the most effective casting method, ensuring efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and the desired performance of the final plastic product.
 When selecting the appropriate method for casting plastic, understanding the final product applications and requirements is crucial. Different applications such as automotive components, consumer goods, or industrial parts necessitate distinct characteristics in the produced plastic. For instance, according to a recent report by the Plastics Industry Association, the automotive sector is projected to consume approximately 27% of all plastics by 2025, highlighting the demand for materials with high strength, durability, and lightweight properties. Therefore, methods that ensure optimal mechanical performance, such as injection molding, are often preferred in this sector.
When selecting the appropriate method for casting plastic, understanding the final product applications and requirements is crucial. Different applications such as automotive components, consumer goods, or industrial parts necessitate distinct characteristics in the produced plastic. For instance, according to a recent report by the Plastics Industry Association, the automotive sector is projected to consume approximately 27% of all plastics by 2025, highlighting the demand for materials with high strength, durability, and lightweight properties. Therefore, methods that ensure optimal mechanical performance, such as injection molding, are often preferred in this sector.
 Furthermore, the requirements of the final product can significantly influence the casting method chosen. For example, in applications where precision and intricate design are paramount, techniques like rotational molding or 3D printing may be employed. A study published in the Journal of Applied Polymer Science points out that 3D printing can reduce material waste by up to 60%, making it an attractive option for custom or small-scale production runs. Ultimately, careful consideration of the end-use requirements—including thermal and chemical resistance, dimensional tolerance, and production volume—will guide manufacturers in selecting the most effective casting method for plastic production.
Furthermore, the requirements of the final product can significantly influence the casting method chosen. For example, in applications where precision and intricate design are paramount, techniques like rotational molding or 3D printing may be employed. A study published in the Journal of Applied Polymer Science points out that 3D printing can reduce material waste by up to 60%, making it an attractive option for custom or small-scale production runs. Ultimately, careful consideration of the end-use requirements—including thermal and chemical resistance, dimensional tolerance, and production volume—will guide manufacturers in selecting the most effective casting method for plastic production.