Choosing the right plastic for molding applications is crucial for success. The right material ensures quality and durability. Different options exist, each with unique properties.
Factors to consider include the intended use, cost, and manufacturing process. Some plastics offer flexibility while others are rigid. Color and texture also play a role.
A common mistake is overlooking long-term performance. Sometimes, a cheaper option may not last. This choice might lead to higher costs later. Reflecting on these aspects can lead to informed decisions. Selecting the correct plastic for molding can significantly impact the final product.
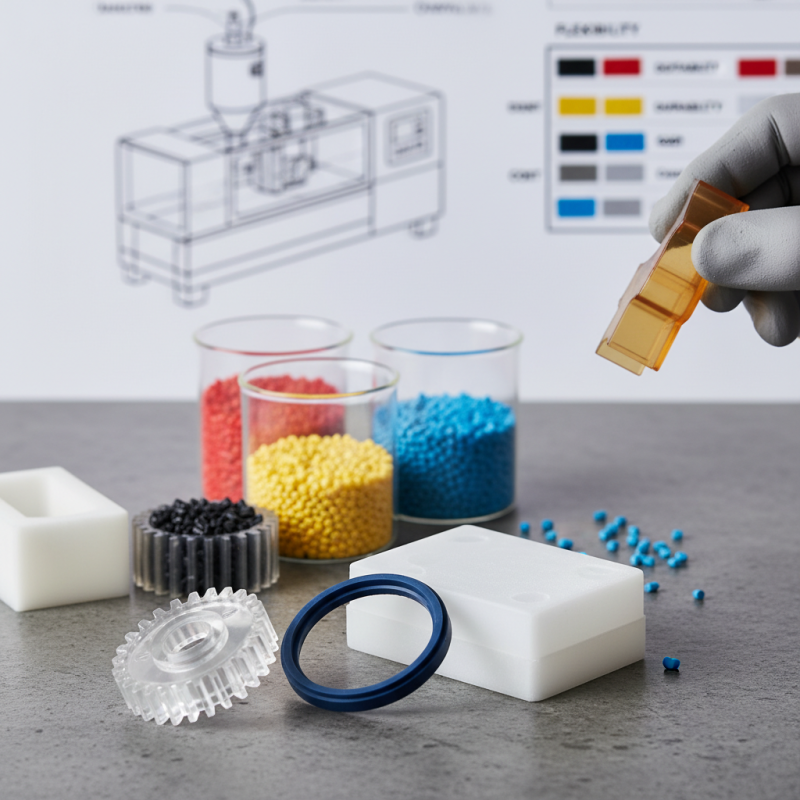
When selecting plastics for molding applications, it’s crucial to understand their diverse characteristics. Thermoplastics, like ABS and polycarbonate, are widely used for their flexibility and toughness. They can be easily shaped and reshaped, making them suitable for various products. However, thermoplastics can be sensitive to heat. Overheating may weaken the final product.
On the other hand, thermosetting plastics like epoxy and phenolic undergo a permanent chemical change when heated. They offer strength and thermal resistance, making them ideal for high-heat applications. Yet, their rigidity can be a limitation for designs requiring flexibility. This trade-off demands careful consideration.
Biodegradable plastics are gaining attention for their eco-friendliness. They help reduce environmental impact, yet their durability is often less compared to traditional plastics. It's vital to evaluate the application needs thoroughly. Often, the choice isn't straightforward and involves balancing strength, flexibility, and environmental considerations. In some cases, unexpected challenges may arise. Planners must remain adaptable to feedback during the prototyping process.

Choosing the right plastic for molding applications requires careful consideration of key properties. One major factor is the plastic's melting temperature. For instance, materials like polyethylene have lower melting points, making them easier to process. This can speed up production time. However, this may lead to reduced durability under high temperatures.
Another essential property is tensile strength. High tensile strength plastics, such as polycarbonate, are ideal for parts needing toughness. The industry standard indicates that polycarbonate has a tensile strength of about 70 MPa. This durability is crucial for components in automotive or electronics. Yet, using stronger materials can complicate the molding process. It often requires more precise machinery or dies.
Impact resistance also plays a vital role. Plastics like ABS are known for their ability to withstand shocks. They are commonly used in consumer goods. However, selecting these plastics can be a double-edged sword. While they perform well, they may not be suitable for intricate designs. These realities remind us that every choice carries trade-offs, necessitating a reflective approach in material selection.
Choosing the right plastic for molding applications can be challenging. Several factors play a crucial role in this decision. The application itself is paramount. Different plastics offer various properties, such as durability, flexibility, and heat resistance. Knowing the intended use can guide selections effectively.
Environmental factors are also critical. Some plastics perform poorly in extreme temperatures or moisture. Understand the conditions your product will face. This information can prevent costly mistakes.
Additionally, consider the production process. Some materials are easier to mold than others. This can save time and resources in the long run.
Cost is another significant factor. While it might be tempting to choose cheaper options, reflect on the long-term impact. Inferior materials may fail sooner, leading to additional expenses.
Also, regulations surrounding safety and recyclability should be in your thoughts. Ensure compliance with industry standards, as overlooking these can create bigger issues down the line.
When considering plastics for molding,
cost and
availability are paramount.
Different materials vary widely in price. For example,
polycarbonate can cost around
$3 to $4 per pound, while
polypropylene ranges from
$0.75 to $1.50. These differences can influence production budgets significantly.
Availability can also impact project timelines. Certain resins may have supply chain issues
due to factors like global demand or natural disasters. In 2021, a report indicated that
44% of manufacturers experienced
material shortages, affecting production schedules. It's crucial to assess both
local and global supply lines before choosing a plastic.
Ultimately, understanding the market trends helps in selecting the right plastic. Some materials,
such as ABS, have more stable pricing due to higher availability.
However, this security can mask potential performance shortcomings. Relying solely on price might lead
to compromises in quality and durability. Balancing cost and material performance is a
complex decision.
Choosing the right plastic for molding can be tricky. Many people overlook important factors. One common mistake is not considering the application requirements. For instance, flexibility and durability may vary significantly between plastic types. This can lead to product failure or unnecessary costs.
Another mistake is ignoring the environmental conditions. The chosen plastic must withstand specific temperatures and humidity levels. Many forget to ask about compatibility with other materials. This oversight can compromise the entire molding process. Additionally, underestimating the importance of color stability might result in fade over time.
Lastly, some choose plastics based solely on price. While cost is a factor, it shouldn’t be the only one. Quality and performance are equally important. We often see products failing due to poor plastic choices, which can harm a brand's reputation. Investing time in research is crucial. Proper selection can save money and enhance product quality.